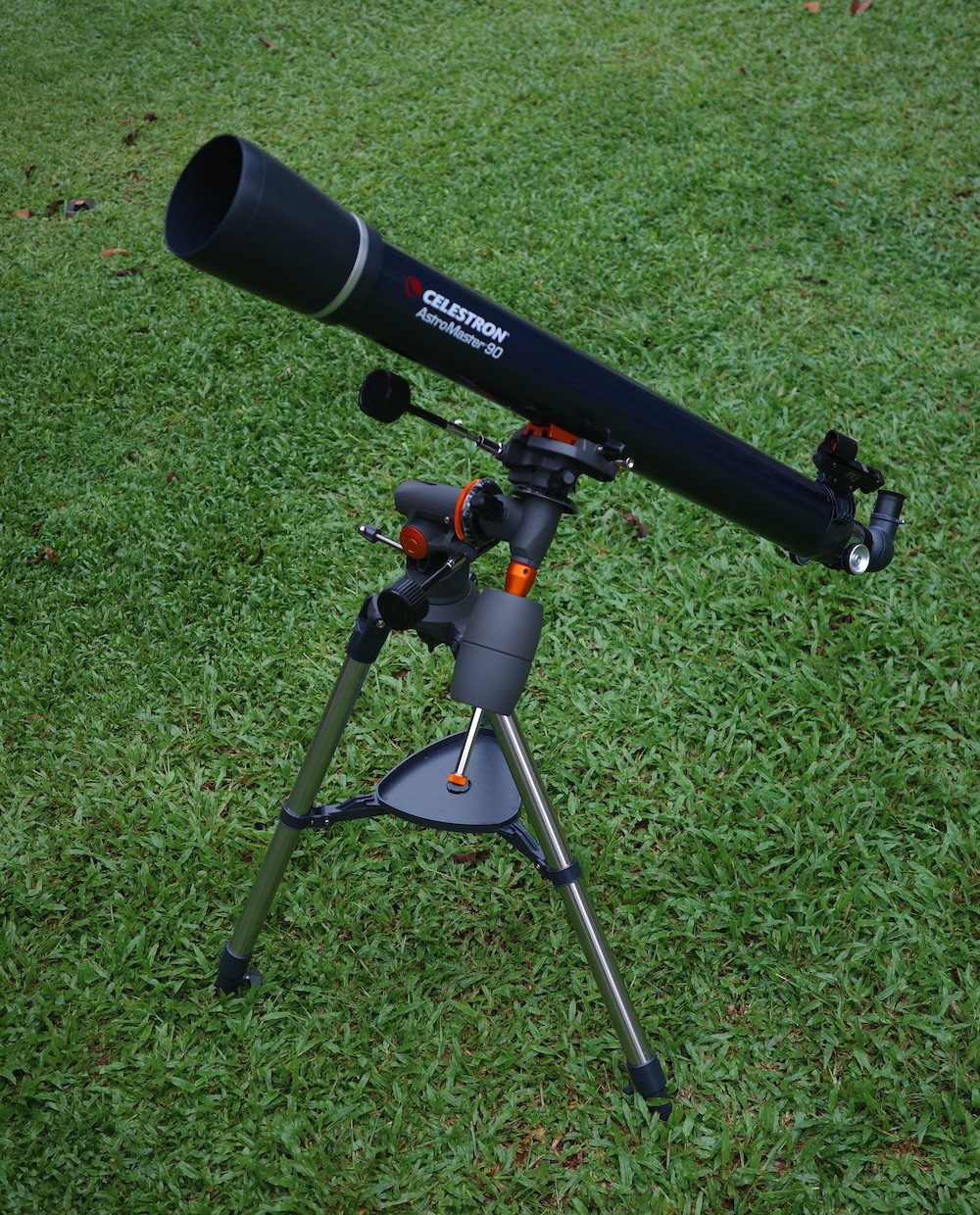
The Optical Tube
The Celestron AstroMaster 90EQ is a 90mm (3.5”) f/11 achromatic refractor telescope with a focal length of 1000mm. The 90EQ, like most achromats, has a Fraunhofer configuration with crown and flint glasses for the objective lens.
At this size and relatively slow focal ratio of f/11, chromatic aberration is kept at bay on all but the brightest targets. I noticed slight purple halos only around the Moon, Jupiter, Venus, and bright stars. Otherwise, the 90EQ had no trouble rendering sharp detail and pinpoint stars.
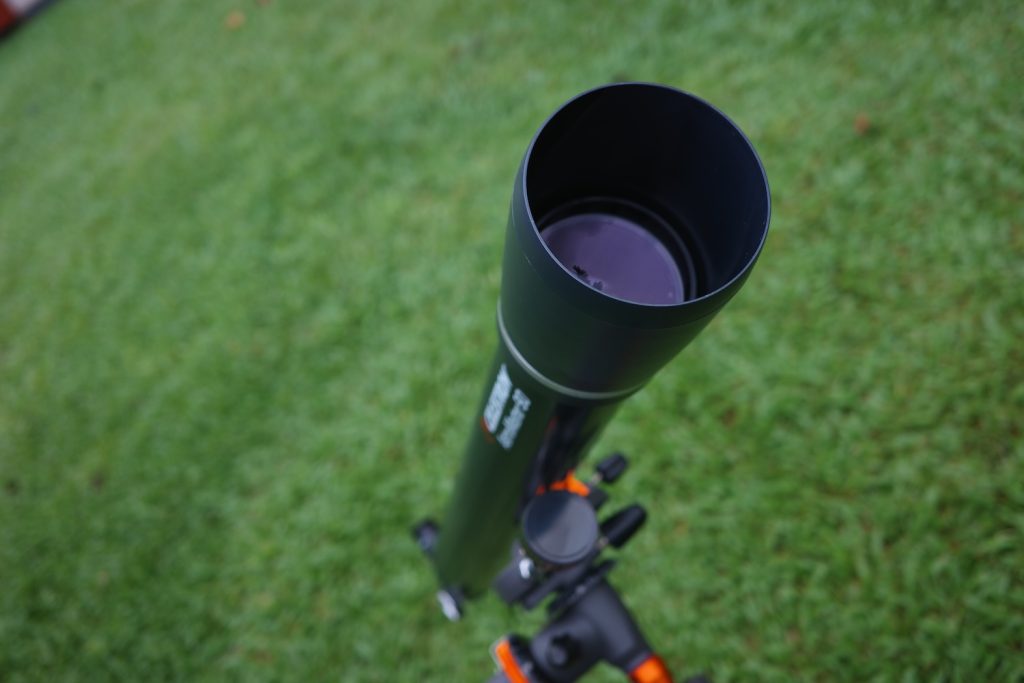

The lens cell seen in the above picture is plastic and is not able to be adjusted should the telescope’s collimation be seriously disturbed. But I think this is unlikely to ever be a problem since refractors hold collimation pretty well.
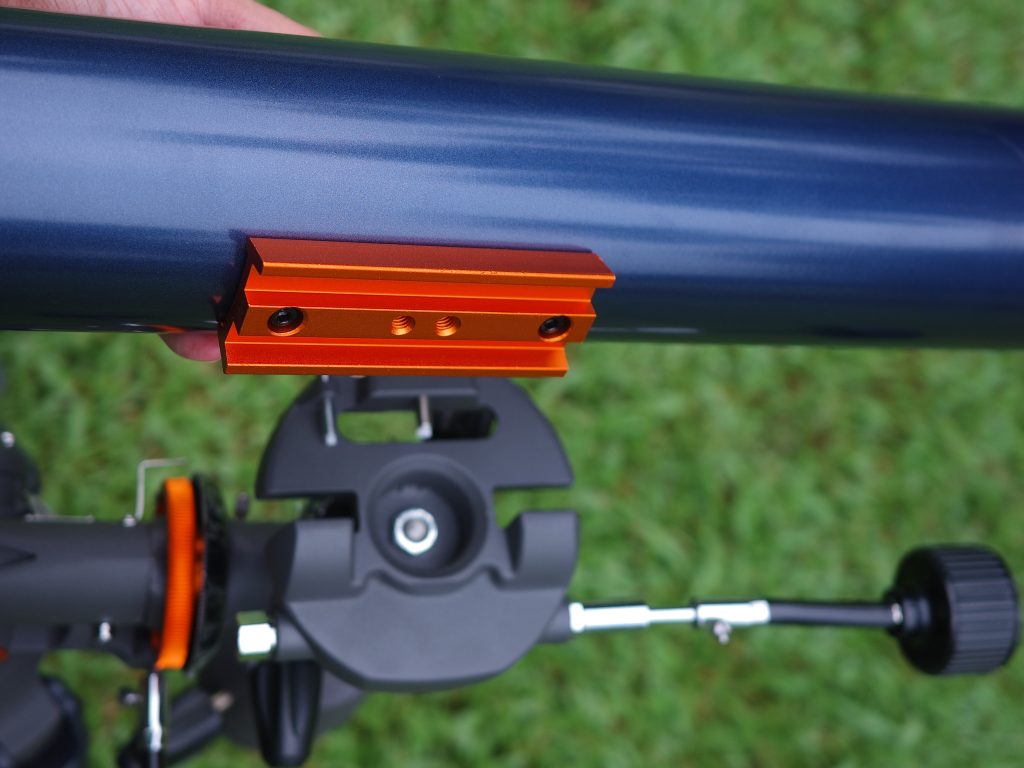

One of many signs of Celestron’s cost-cutting measures that I’ve noted is the short Vixen-style dovetail plate bolted to the bottom of the AstroMaster 90EQ’s optical tube. There is no way to rotate the tube in any rings to move the eyepiece angle, nor slide the whole thing along for balance. The universally standard dovetail at least allows us to easily attach the telescope to a different mount if we wish.
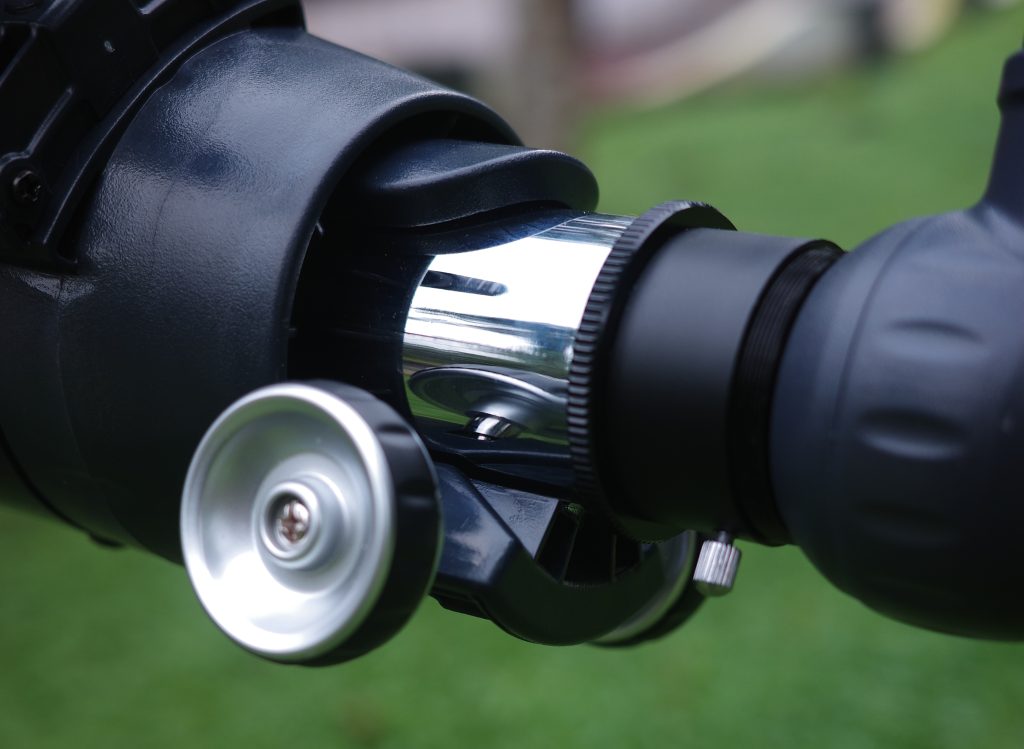

The 1.25″ rack and pinion focuser is made mostly of plastic, which works okay if I don’t use any heavy or expensive eyepieces, though it can sag and wobble somewhat.
Accessories Provided

The Not-so-Good Amici Prism and The Eyepieces
The Celestron AstroMaster 90EQ refractor telescope is equipped with a 1.25” Amici prism diagonal that is designed for terrestrial viewing. It has a unique shape and grip that is designed to accommodate people like myself who grab and hold it like a handle.
The body is plastic, and the Amici prism itself is, upon testing, not of high quality, causing internal reflections and glare. The Amici prism design also inherently produces a bright spike on bright objects.
What’s more is that Celestron’s cheap Amici prism is so undersized that it actually vignettes my view with low-power eyepieces like a 32mm Plossl, which explains Celestron’s unusual choice to provide a 20mm 3-element eyepiece for “low” power (50x).
50x magnification is quite a lot for such a small instrument, and the 50-degree apparent field of view of both eyepieces means the true field the 20mm ocular provides with the 90EQ is only 1 degree across, or about twice the width of the full Moon.
For high power, we get a 10 mm 3-element eyepiece for 100x.
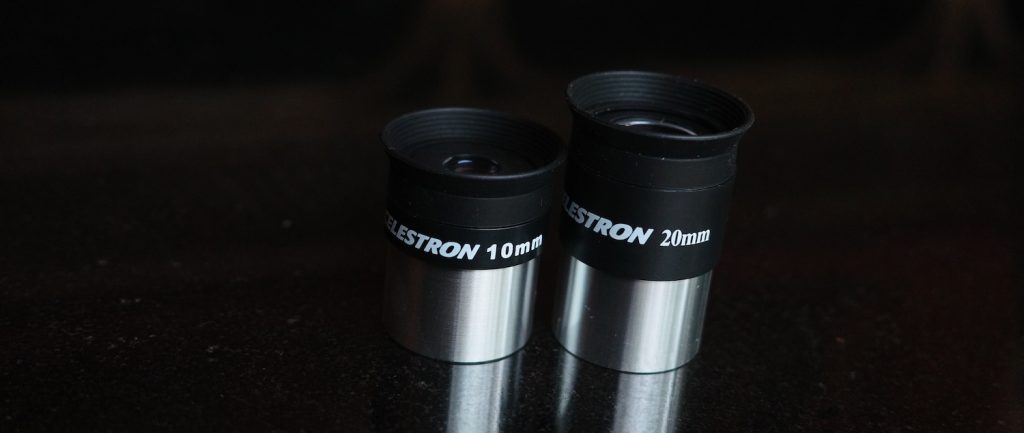

Both of these 1.25” eyepieces are of acceptable quality and provided me with sharp images, though their performance is bottlenecked by the low quality of the Amici prism.
The Red Dot Finder & The Complexities
To aim the telescope around the sky, the AstroMaster 90EQ comes with a standard, generic “StarPointer” red dot sight powered by a CR2032 battery.
The provided red dot finder is great, and I consider it to be an actual ad-hoc upgrade from the original low-quality plastic sights that were originally shipped with the AstroMaster line.
Unfortunately, the retrofitted bracket that used to attach the red dot sight to the AstroMaster 90EQ’s tube is cheaply made and often misshapen enough to make it difficult to align the finder with the telescope. Not being able to properly align the finderscope can make trying to point the 90EQ at anything frustrating or even impossible.
Making a DIY fix, which is what I’d normally do, or buying a replacement finder/bracket is fairly easy to do. But it’s frustrating to me to even think that Celestron created the problem in the first place.
The AstroMaster CG-3 Mount
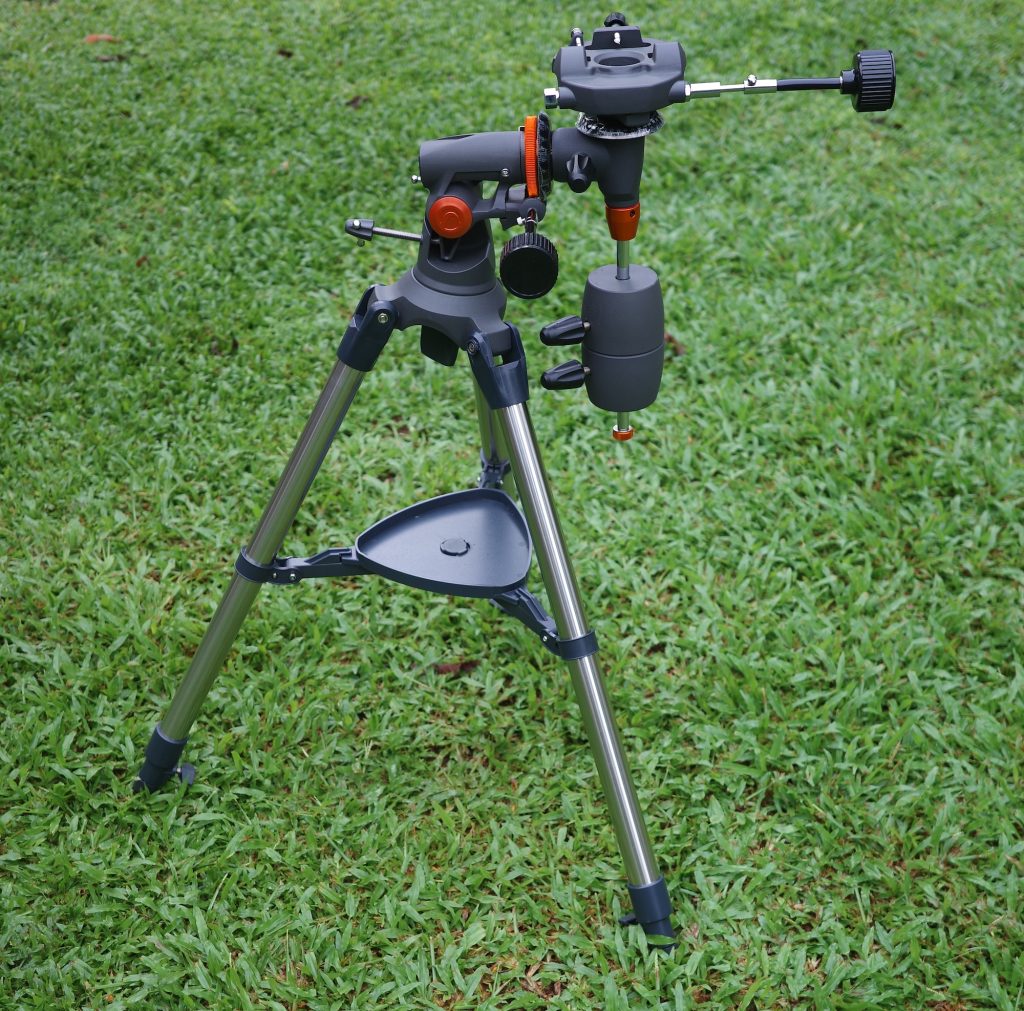

The CG-3 is a typical cheap German equatorial mount with small, decorative setting circles (advertised as a feature but essentially useless). It has 1.25” tubular steel legs, but much of the tripod and fittings, such as the leg locks and the accessory tray, are made of cheap plastic that is easily damaged.
Polar Alignment
The GG-3 also has fine adjustments for polar alignment, which need to be done after you assemble the telescope and level the tripod. There are no provisions for a polar scope, so your polar alignment is going to be fairly inaccurate, but for a telescope that’s not for astrophotography, this isn’t a big deal.
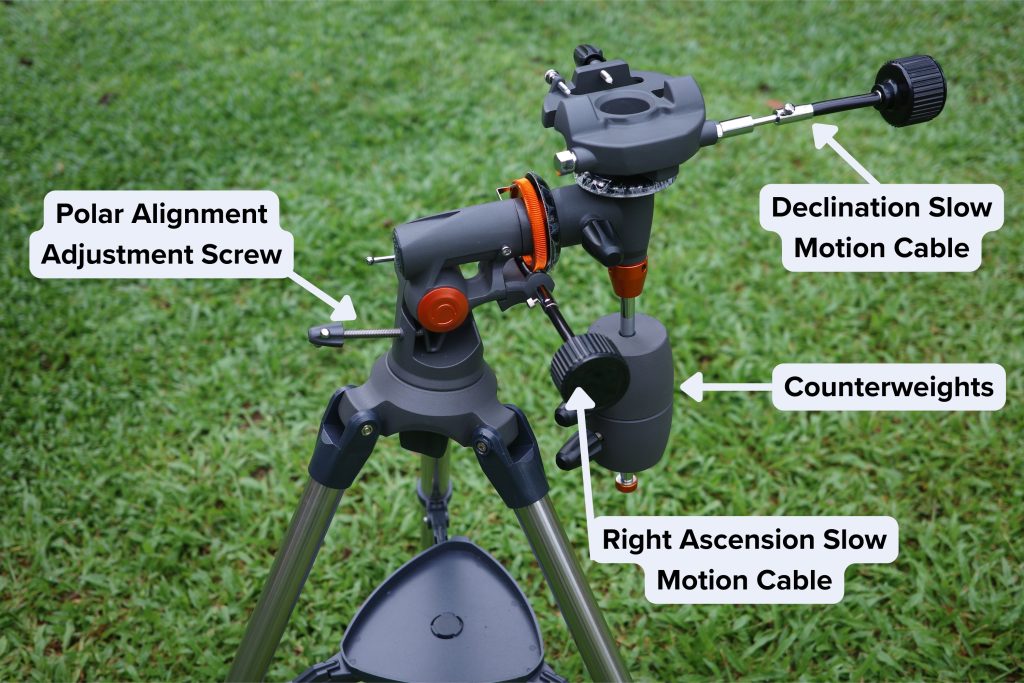

Balancing
The CG-3 also has to be balanced correctly with the telescope optical tube, as with any equatorial mount.
Normally, you’d have to slide the 90EQ’s tube forward-backward in some kind of tube rings or move the dovetail bar itself for balancing in declination. But the 90EQ’s Vixen-style dovetail bar is so short that you basically cannot adjust for balance on the declination axis, though the default position is just fine.
Balancing in right ascension is done with the two provided counterweights. You can leave the counterweights installed or mark the counterweight shaft with a permanent marker or tape to avoid having to figure out balance every time you assemble your telescope.
Usage
After polar alignment and balancing are done, you aim the CG-3 around the sky by loosening the clutches and then locking them when you are close to your target.
As with most manual mounts, it thankfully has flexible slow-motion cables for both axes; you turn the right ascension cable to track targets throughout the sky, and both slow-motion cables are used for finely pointing the telescope after the clutches are locked.
You can add a cheap motor drive such as Celestron’s “Logic Drive” to obviate the need for manual tracking altogether, though neither the mount, telescope, nor drive are any good for long-exposure astrophotography.
While cheaply made, a little complex to use, and certainly not the steadiest, the CG-3 mount is alright for the AstroMaster 90EQ. It can be improved by avoiding extending the tripod legs all the way, filling the legs with foam or sand, and putting a heavy item such as weights or a water jug on the accessory tray to lower the telescope’s center of gravity.
Should I buy a Used Celestron AstroMaster 90EQ?
A used Celestron AstroMaster 90EQ is a decent scope if it is available at a low price.
However, older units have a circular plastic sight that is essentially useless and gets in the way of installing a proper finder, which you may want to avoid.
The plastic parts on the 90EQ are easily damaged, and you should make sure the lens is free of any chips or cracks.
There is little that can go wrong with a used unit that won’t be immediately obvious to even the most casual shopper.
Alternative Recommendations
The Celestron AstroMaster 90EQ provides poor value in its price range compared to many of the other high-quality reflectors, refractors, and catadioptric telescopes available.
Under $300
Dobsonians
- The Sky-Watcher Heritage 130P has significantly more light-gathering ability, a wider field of view, and a sturdier mount than the AstroMaster 90EQ, and is extremely portable thanks to its collapsible tube and tabletop Dobsonian mount.
- The Zhumell Z114/Orion StarBlast 4.5 Astro has larger aperture, a wider field of view, a steadier mount, and a much lower price tag than the AstroMaster 90EQ.
- The Zhumell Z100/Orion SkyScanner 100 are very inexpensive and either provide similar light-collecting power to the AstroMaster 90EQ but with a huge field of view, rock-solid mount, and a very low price tag.
Refractor
- The Celestron StarSense Explorer LT 80AZ Refractor isn’t perfect and has slightly less aperture than the AstroMaster 90EQ but it is considerably easier to aim around the night sky.
$300-$500
Dobsonians
- The Sky-Watcher Heritage 150P has significantly more aperture and is drastically easier to use than the AstroMaster 90EQ, as well as being extremely portable; it’s essentially an upsized Heritage 130P.
- The Sky-Watcher Virtuoso GTi 150P shares the optics, accessories, and design of the Heritage 150P but adds fully motorized GoTo and tracking, controlled by your smart device and still able to be aimed freely without ruining the accuracy of its computerized pointing abilities. The Virtuoso GTi 130P uses the same mount as the GTi 150P but with a Heritage 130P optical tube.
- The Orion SkyQuest XT6 has a rock-solid Dobsonian mount that requires neither a table nor tripod, a large 6” primary mirror, and a high-quality 2” Crayford focuser. The AstroMaster 90EQ is practically a toy by comparison.
Refractors
- The Popular Science Celestron StarSense Explorer DX 100AZ Refractor and Celestron StarSense Explorer DX 102AZ have more chromatic aberration than the AstroMaster 90EQ but include slightly better accessories and simpler mounts with the added bonus of a much wider field of view, slightly more aperture, and easy aiming with Celestron’s StarSense Explorer technology.
Aftermarket Accessory Recommendations
The stock 1.25” Amici prism that comes with the AstroMaster 90EQ needs to go immediately. You should replace it with a quality 1.25” star diagonal, such as the Celestron 94115-A Prism Star Diagonal. While a decent prism diagonal can seem expensive, it will drastically improve your views through the 90EQ’s otherwise-great optics. Cheap mirror diagonals will provide a less-than-sharp image.
A 32mm Plossl eyepiece coupled with a new star diagonal will provide 31x magnification and a wider true field of 1.7 degrees, ideal for finding and viewing deep-sky objects with the AstroMaster 90EQ. The stock 20mm and 10mm 3-element eyepieces are just fine for the rest of your eyepiece kit.
A 6mm “goldline” or “redline” will provide 167x, which is about the limit of what a 90mm telescope can handle. Higher power than 100x may show you slightly more on the planets and split closer double stars than the 10mm Kellner but at the expense of providing a shakier and very dim image.
What can I see with Celestron Astromaster 90EQ?
Deep Sky Targets
The Celestron AstroMaster 90EQ is not well-suited for viewing deep-sky objects due to its small aperture and long focal ratio.
- Galaxies appear as faint smudges with only 90mm of aperture, even under dark skies, with the exception of the brightest galaxies, such as M31 and M82, which show hints of dust lanes and other detail.
- Globular star clusters and planetary nebulae are unresolved, dim, and faint fuzzies with the 90EQ, regardless of the light pollution conditions or lack thereof.
- Open star clusters like M35 and M11 looks attractive in the AstroMaster 90EQ, but the telescope’s limited field of view due to its long focal length means that larger clusters like the Pleiades or Double Cluster are not nearly as pleasing as what a low-power, wide-field instrument of similar aperture show them to be.
- The brightest nebulae, such as Orion (M42) and the Lagoon (M8), reveal their brighter gas clouds and interior star clusters, but their fainter wispy regions are less obvious, and the view is far from as stunning as when viewed through a larger telescope, especially if we are stuck under light-polluted skies.
- Double stars are a good test of your observing skill and the steadiness of your current seeing conditions. Thousands of double stars are fairly easy to find with the AstroMaster 90EQ, appearing as colorful pinpoints at high magnification.
Solar System Targets
The AstroMaster 90EQ’s sharp optics make it a decent performer on Solar System objects (i.e., the Moon and planets).
I can just barely resolve the phases of Mercury on a good night; Venus is far easier.
The Moon always delights with craters, mountains, ridges, and other details on any given night.
Mars’ polar ice cap is visible most of the time with the 90EQ. On the best nights when Mars is at its closest and seeing conditions permit, I can also resolve some dark markings on its surface.
Jupiter’s cloud banding, smaller atmospheric features like storms, and the Great Red Spot is seen with the AstroMaster 90EQ, along with its four large Galilean moons. Io and Europa are hard to resolve as clear disks, as are their high-contrast shadows when they transit in front of Jupiter. But Ganymede and Callisto is in no trouble to see as tiny orbs when they transit, with their shadows following close behind.
I can also resolve the rings and cloud belts of Saturn, the Cassini Division in the rings, and a few moons around Saturn as well.
Uranus and Neptune appear as fuzzy dots, with disks too small to resolve and moons too faint to see; Pluto is similarly out of reach of a telescope this small.