
Decades ago, even a small refractor telescope with two-inch-wide achromatic objectives mounted on a simple altaz fork was a severe investment. Nowadays, we can find similar offerings for 100 bucks, and large commercial Dobsonian reflectors with apertures of 6 to 12 inches are becoming very affordable. There are more telescopes than ever for beginners, but I’m equally sad that a great many of them are rubbish.
The “Department Store Refractor” is an archetype of a generally very poor telescope—essentially a toy sold to parents who don’t know better, usually with poor optics and poorer mounts. But this term, related to the more descriptive “Hobbykiller Telescope,” can also be applied to some big-name telescopes sold by Celestron, Sky-Watcher, e.t.c
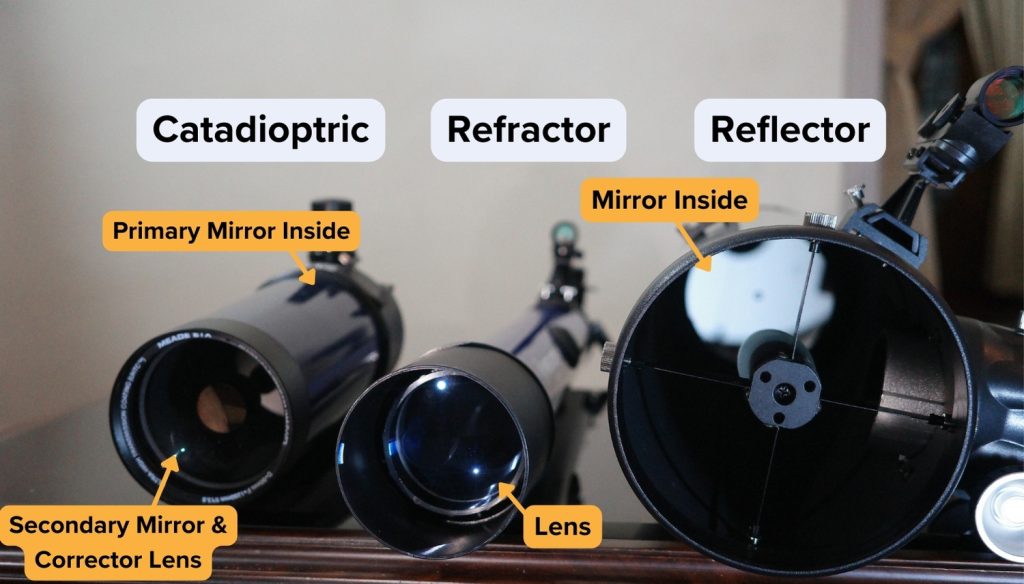
The truth is that a great many of these refractor telescopes are not horrible, optically. Most of them usually use usually half-decent, if somewhat small glass achromatic (false-color-reducing) doublet lenses and can produce some crisp images.
The trouble is often in the accessories—which tend to be of poor quality, sometimes even using the deprecated 0.965” standard. Much ink has been spilled about these accessories. Even with telescopes using pretty poor accessories, the telescopes are still optically superior to what Galileo, Kepler, Messier, and Huygens had to play with, and each of them made some of the most important observations in astronomy.
For a cheap instrument, I’d even forgive somewhat-poor optics up to a point. For me much more important is the mount—it determines whether a telescope remains a useful and engaging observing instrument or stay unused in the attic. A wobbly mount, one which refuses to hold steady, which drifts, drops, or sags, which shakes if I look at it wrong—that is the real hobby killer. And it is all too common in beginner telescopes of all optical configurations.
How can we avoid hobbykiller mounts? The short answer to that from me is “Avoid any telescope on a tripod by default; get a Dobsonian.” You can, of course, find plenty of decent beginner telescopes on tripods, but the easiest way to avoid the worst ones is to steer clear of them. The long answer follows.
- 1. Altitude/Azimuth (Alt-Az) Mounts
- 2. Equatorial (EQ) Mounts
- 3. Infinite Axis (Ball) Mounts
- 4) Hybrid Mounts
- The Problem with Tripods, and Why Avoid Them
- The Versatility of Dovetails
- Unmounted or Handheld Telescopes
Let’s take a look at some of the mounts, which are often shipped with beginner telescopes. The motions of a mount, that is, the axes through which they rotate, come in three main varieties:
1. Altitude/Azimuth (Alt-Az) Mounts
These go vertically (up, down) and all around horizontally. The telescope swivels around 360 degrees along the horizontal plane, all around the horizon. It’s altitude axis allows us to view anything from the horizon (0°) to the zenith (top of the sky, 90°).
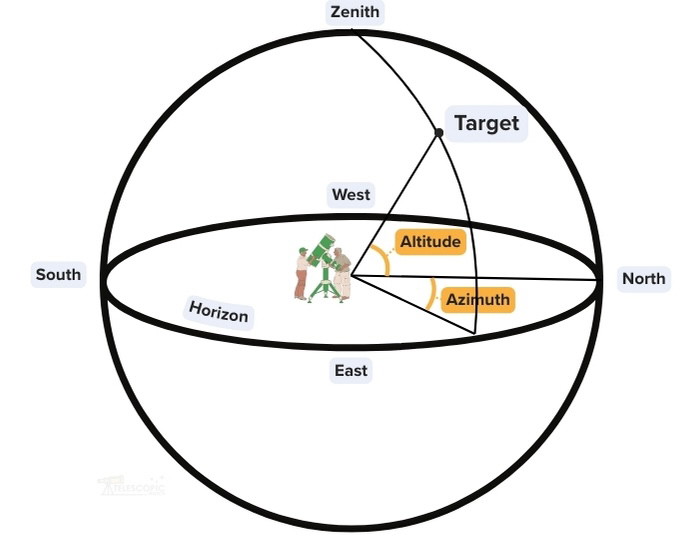
One trouble I’ve faced with these is the difficulty in pointing at objects within “Dobson’s Hole,” a region of the sky near the zenith (directly overhead) where it becomes very difficult to point and track smoothly because the azimuth axis needs to do a lot more turning.
Altitude-Azimuth Mount Types
Probably the majority of cheap beginner telescopes come on some variety of altitude-azimuth mount. Let’s look at some of the most common types and their pros and cons. There are other unique designs besides what follows, and sometimes you’ll find variants of each of these with slow-motion knobs and cables.
1) Dobsonian: The One True Beginner Telescope Mount
By far the best mounting option for a beginner reflector telescope is a Dobsonian or a tabletop Dobsonian.
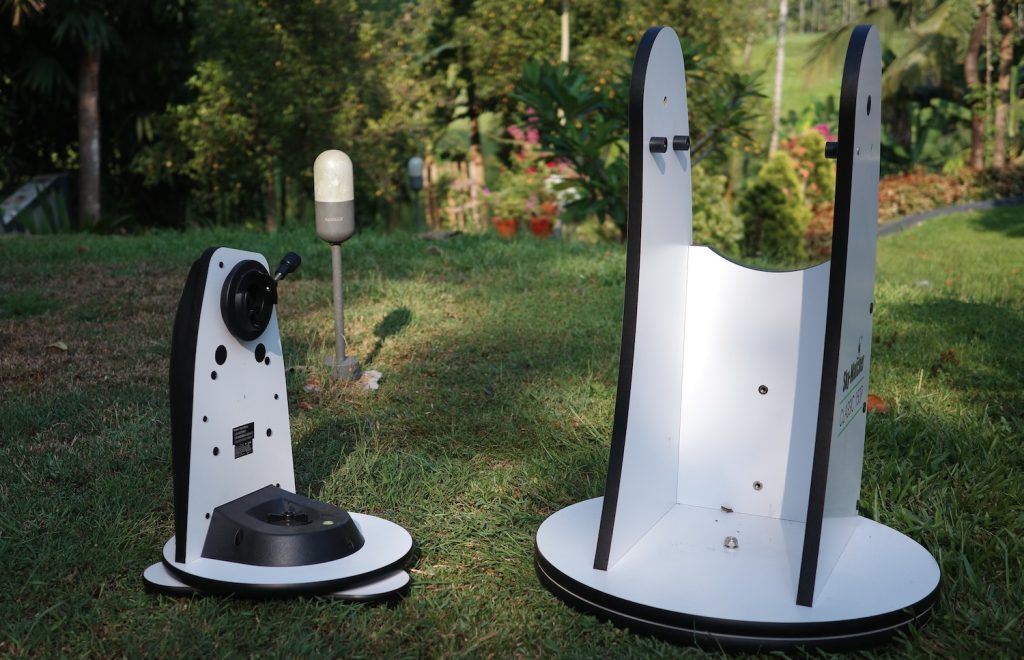

These mounts are almost always paired with Newtonian reflector telescopes (particularly good bang for your buck as even large aperture Newtonians can be made cheaply). The Newtonian-Dobsonian telescopes are, by far, the best bang for your buck of any kind of telescope. I’ve also occasionally seen Maksutov Cassegrains (and even, in amateur telescope-making circles, Refractors) with a Dobsonian-type mount, but they are rare.
A Dob is a mechanically simple, elegant altitude-azimuth design. A lazy-susan mount provides the “all-around” motion, and a rocker box and simple friction-fit bearing provide the “up, down” motion. The bearings are simply Teflon strips.
The construction is made of wood or particle board. They are exceedingly cheap to manufacture compared to any other mount that is worth using, and yet they are incredibly effective.
A Dob allows us to simply grab the telescope and push it to where we want it, and it’ll stay there. Even at very high magnifications (200x, 300x), shaking and wobbling are manageable, and the motions are smooth enough to track with.
2) Photo Tripod Style Alt-Az
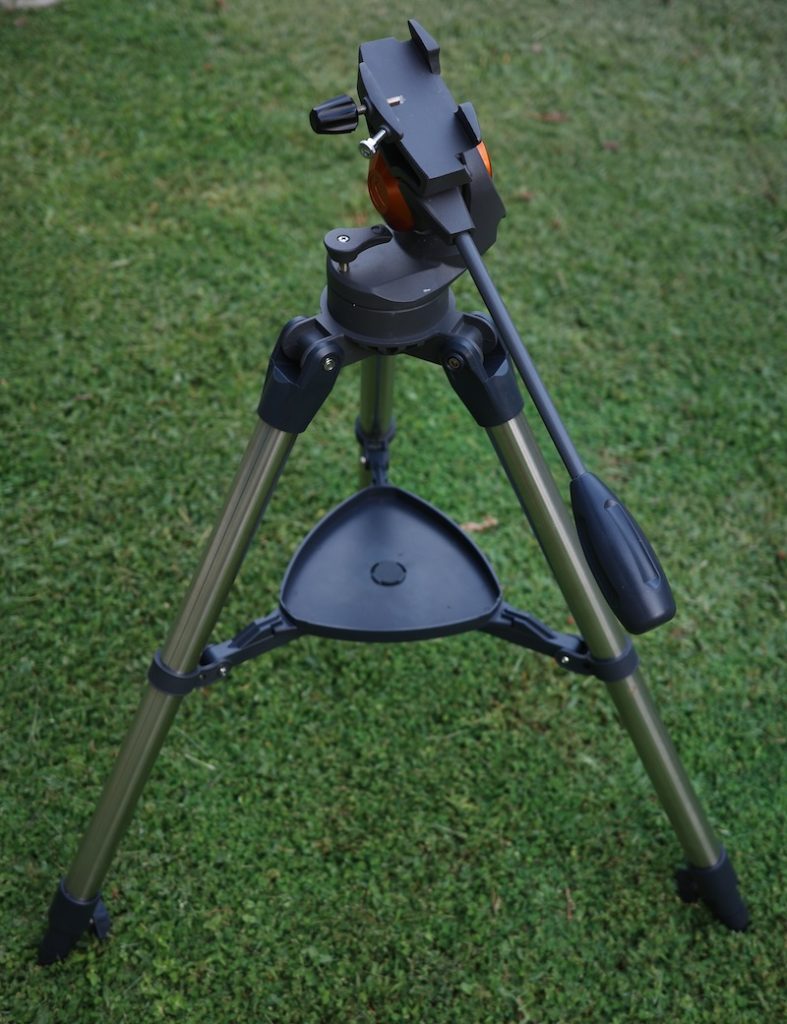

This is one of the most common types. The mount is essentially a photo tripod adapted to carry a telescope. It may be a little heavier and sturdier than a standard photo tripod. It may be fitted to accept a Vixen dovetail (as in the AstroMaster AZ telescopes), or it may be a cheap, finicky thing that is screwed onto the telescope.
The photo tripod style is marked by a handle coming out the back, as seen in the above image, which is used to adjust the mount. A good photo tripod will also have knobs that can be tightened enough to prevent the telescope from drifting when pointed high in the sky.
Some small telescopes and binoculars have fittings for a photo tripod, so a standard photo tripod can be used. However, such a mount is inherently impossible to balance.
3) Simple Hinge Alt-Az
Here, the altitude axis is a simple hinge that goes back and forth and may have a tension knob. These are awful; avoid them. They have the same balance issues as the photo tripod, except worse, and they’re often built incredibly poorly. Not recommended.
Note: some hinge or photo-tripod-style mounts might include a large counterweight to keep the telescope in balance. Though I can’t speak to the stability of those systems, they can at least be balanced to prevent drifting.
4) Simple Fork/Yoke Alt-Az
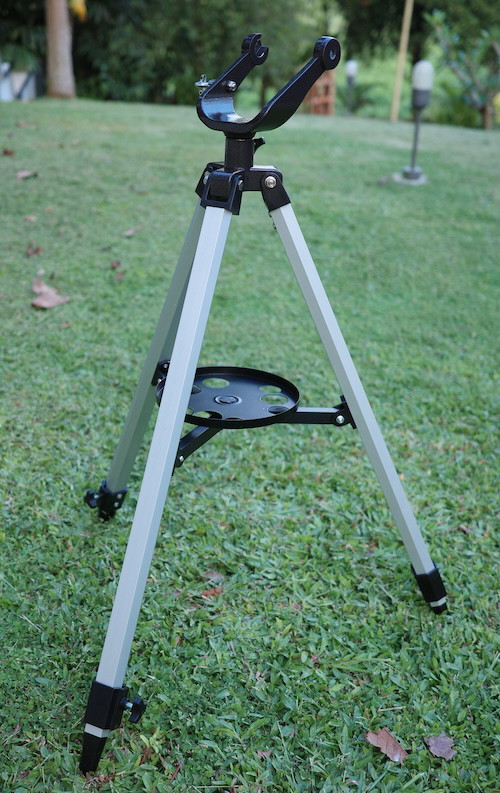

Mechanically very simple. The telescope is screwed between the prongs of a fork, which is mounted on an azimuth bearing in the tripod. The fork is usually offset backward so that the telescope can be pointed straight up without running into the tripod.

If the fork is sturdy and metal, it can be worth using and is probably the best altaz mount for a beginner lens-based refractor telescope. If it’s thin, flimsy plastic, you’re out of luck.
5) Go-To Fork Alt-Az
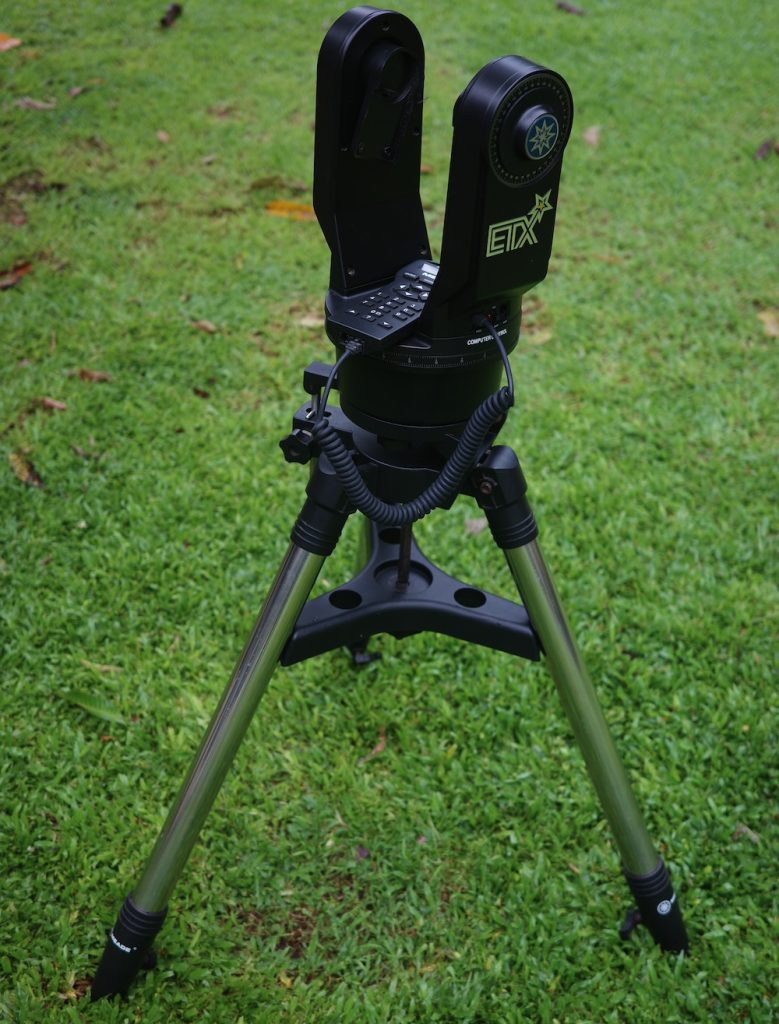

Here, the fork and the base are much sturdier and contain motors to automatically move the telescope in altitude and azimuth. Here, you’ll often find undermounted beginner telescopes where the mount itself is a capable device, but it’s carrying a telescope too heavy for it to reliably move and track without issue.
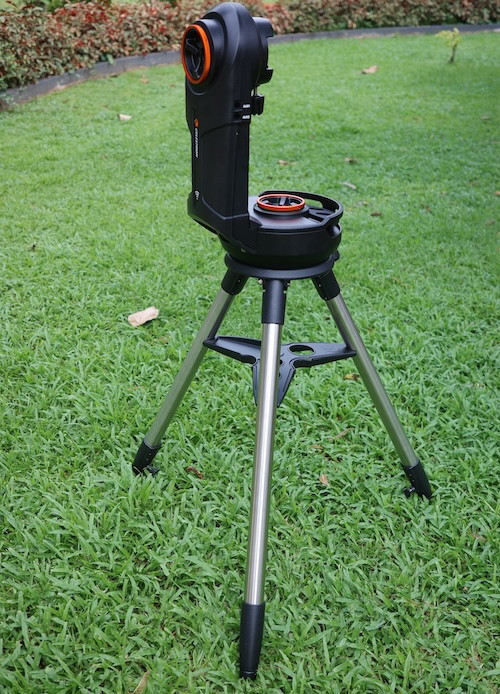

Half-forks are a more common variant of Go-To forks, especially in beginner telescopes, where the telescope is supported by a single-altitude arm rather than two. These are mostly used with Cassegrain telescopes, but they can be found with Newts and Refractors as well. As long as the mount isn’t too undersized for the telescope it carries, they are fairly decent.
However, I also need to clarify here that I don’t recommend computerized telescopes for beginners. More on this later.
2. Equatorial (EQ) Mounts
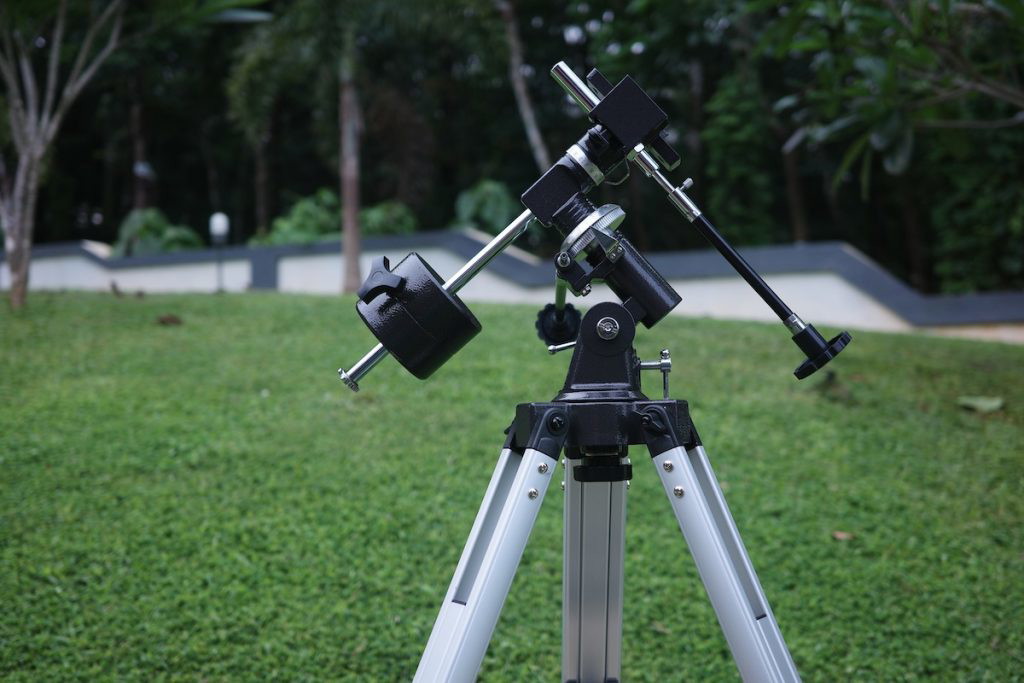

These telescopes are conceptually the same as tilting an altaz telescope at an angle, so that the azimuth axis points not straight up but at the celestial poles. If you don’t immediately know what I mean by that, do not fret, but know that an EQ mount is likely not the best choice for you.
Equatorial mounts are usually a lot more complicated to set up and use, but they have the distinct advantage that a single axis can be rotated to keep up with the rotation of the Earth.
For the same price as a telescope on a really good equatorial mount, you can get a much larger Dobsonian telescope, and you’ll have more fun with it. The only time when an equatorial mount is really important for a beginner astronomer is if they must have the ability to track and take astrophotos.
Equatorial (EQ) Mount Types
There are basically two kinds of equatorial mounts:
Go-To Forks and Half-Forks (uncommon in entry-level telescopes)
Fork mounts are mostly “tilted” on a wedge – essentially an angled plate that converts an alt-az fork’s azimuth axis to a right ascension axis and altitude axis to declination axis. The problem is that the telescope is inherently unstable with this configuration, as the often heavy drive base of the fork is placed at some point well outside the center of its pier or tripod.
If you were to extend the equatorial forks so that they met again at some point above the telescope tube at a second pivot point, you’d have an English yoke mount. The English yoke mount is actually a really clever design. But it’s not portable, and the top of the right ascension axis means the telescope can’t point near the north celestial pole.
Occasionally, designs such as the inverse fork and cross-axis English yoke mount are built, but the only one you’re likely to ever see is the German equatorial mount, or GEM.
German Equatorial Mounts
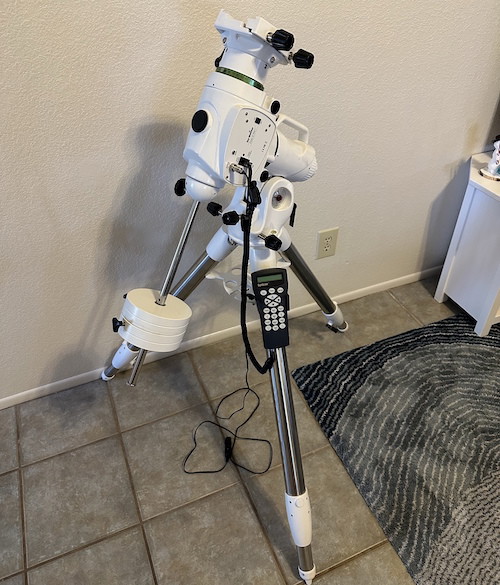

German equatorial mounts are fairly simple in construction and can be used atop tripods.
Even if you get an EQ-mounted telescope that is actually within the mount’s payload range, it will still be frustrating to learn to use properly unless you’re fairly experienced. For most of the time I owned my AstroMaster 114EQ, I never used the mount properly because I didn’t understand how. Only after I had a formal education in amateur astronomy did I understand how to use the equatorial mount properly. But by then, it was so worn out that I ended up getting rid of it.
3. Infinite Axis (Ball) Mounts
These are rare these days, but they are very easy to use. These telescopes are mounted inside or atop a smooth ball, which rests in a cradle.
The telescope can easily be moved to any position in the sky; there are no dead spots at the celestial pole or the zenith where it is difficult to track; and the eyepiece can be rotated to any position.
Newton’s first reflecting telescope and the infamous Edmund AstroScan are examples of this sort of mount.
But Ball-mounted telescopes, such as the Edmund AstroScan, has been out of fashion for the past decade or two, which is kind of a shame. They’re even easier to use than the Dobsonian mount, and they’re a little more versatile. But every commercial telescope ever built that uses this kind of mount has had some caveats. Here are a few drawbacks worth discussing.
- Unlike most other mounts, it’s impossible to adjust the tension or friction on the ball mount. If you find it moves too easily, or if it becomes slightly unbalanced, it isn’t possible to clamp something down and prevent it from rolling out of place. In practice, I found this is mostly only a problem when you’re pointing at the horizon.
- Most ball mounts do not allow for collimation (alignment) of the primary mirror. So if it gets bumped out of place, or ships with it out of place, there’s not much you can do to fix it. I have seen one example of a small ball-mounted telescope that has primary collimation, but it isn’t common.
- The ball gets in the way of sighting along the tube or looking through any kind of finderscope normally placed on the front of the tube. However, this has been worked around by simply lengthening the strut attaching the finder to the telescope tube.
- It is practically impossible to use with optical designs other than the Newtonian reflector.
Still though, for how easy to use they are, I can’t speak too poorly about them, conceptually. The only problem is that you’re not likely to find any new ball-mounted scopes anymore, as after the AstroScan stopped being made around the turn of the millennium, its knock-offs followed suit. A tabletop Dobsonian is a fine substitute, however.
4) Hybrid Mounts
A few alt-azimuth mounts that can be converted to equatorial configurations exist. These broadly fit into two categories:
- The first is the computerized fork-mounted Schmidt-Cassegrain telescopes from Meade and Celestron, which can be converted to an equatorial configuration with a wedge—a special angled plate that tilts the scope.
Older manual fork mounted telescopes can take advantage of a wedge for tracking as they can only do so in the equatorial configuration. Newer units can utilize GoTo for tracking just fine in the alt-azimuth configuration itself without a wedge.
Even for astrophotography, in my experience, fork mounts with wedges are rarely as accurate or easy to set up as a German equatorial mount. Additionally, wedges are expensive and add to the weight, height, and complexity to your telescope. So, if you have a GoTo telescope and can avoid using a wedge, I believe it’d be a right choice to do so usually.
- Sky-Watcher, ZWO, iOptron, Losmandy, and others market mounts that can be converted to an alt-azimuth side-by-side (inverse fork, technically) configuration mount to hold one or two telescopes and then tilted to become a German equatorial mount.
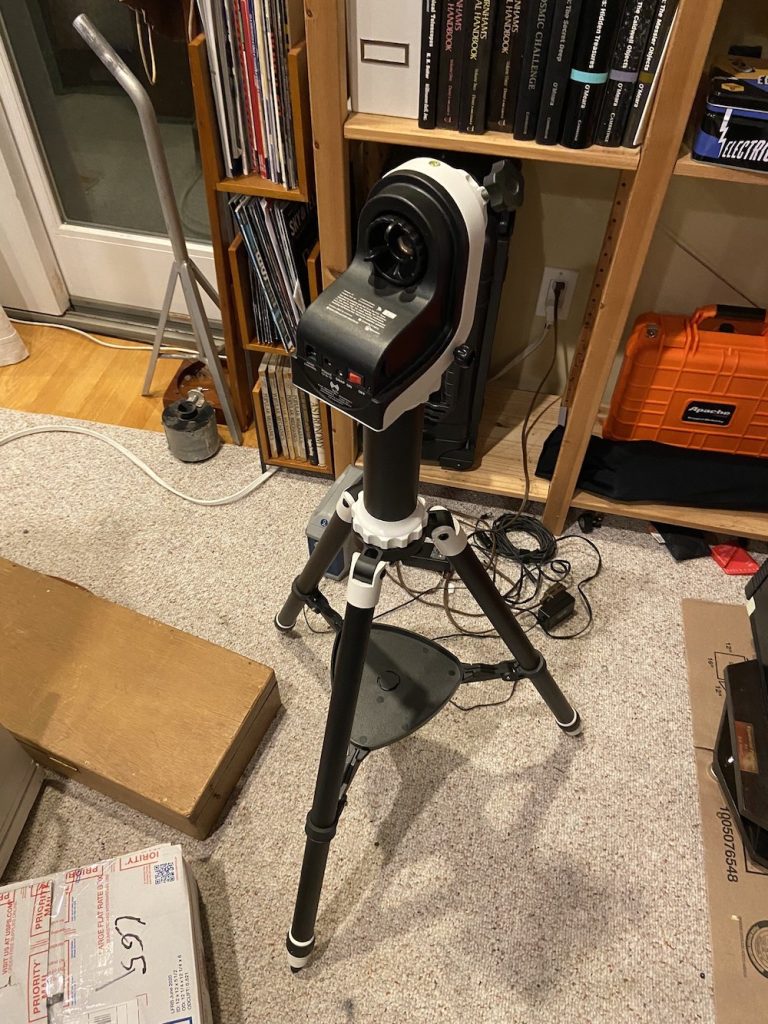

This type of hybrid mount is newer.
The vast majority of these hybrid mounts are GoTos, and many are often based on quality astrophotography mounts. So, if you have the money and want additional versatility for your equatorially-mounted setup, I say, by all means, go with a hybrid mount. However, I need to warn you that you may not need an expensive hybrid mount if you are just using a small telescope for visual observation purposes.
The trouble with beginner telescope mounts is this: A good telescope mount (one that will keep it stable, in balance, and won’t wear out) costs about as much as the telescope it is designed to carry. This is true except for pretty much any mount design, except for one, Dobsonians. The result is that to keep costs down, telescope manufacturers focus on the optics of the telescopes while cutting corners on the mounts and accessories. (Though sometimes they just cut corners everywhere, including the optics, which is how you get utter trash like the PowerSeeker series.)
The Problem with Tripods, and Why Avoid Them
Because of the cut corners in most beginner telescope mounts and the clear superiority of the Dobsonian, I do not recommend any beginner telescope on a tripod, by default. Beginner telescopes are often sold with some pretty awful tripods.
Sometimes, the mount is decent enough, but the tripod it is attached to is dreadful. Springy, loose, and wobbly.

It can be hard to tell for sure just by looking, but in my experience, tripods with thick, round legs are the best. The thin aluminum rectangular legs on many modern beginner telescopes are poor performers because they’re not stiff enough—they’ll twist if you’re trying to move the telescope in azimuth. Wooden tripods are not found in new telescopes anymore, but they may be sturdier than the flimsy aluminum ones.
A few tricks I employ to increase the stability of a tripod:
- Tie a heavy counterweight, something like the weight of a gallon or half of water, to the underside of the top of the mount.
- Spread the tripod legs out as much as possible to keep them slightly under tension.
- Don’t extend the tripod legs, keep them at their lowest length.
Dobsonians and tabletop telescopes do not rely on tripods. They use three small feet to maintain a three-point contact on a surface, but these are not really structural.

A tabletop telescope requires a sturdy table, stool, or chair to mount on. However, they can also use parts of the environment–rocks, walls, the hood of the car you brought it out to the dark site with, etc.

A full-size Dobsonian rests on the ground. Because their wood deforms if it gets too wet, it may be best to lay down a large plastic bag or a tarp to keep it dry in dewy grass. But the telescope is usually long enough that you can easily use it by sitting down in a chair at the eyepiece without a tripod needed to bring it to eye level.
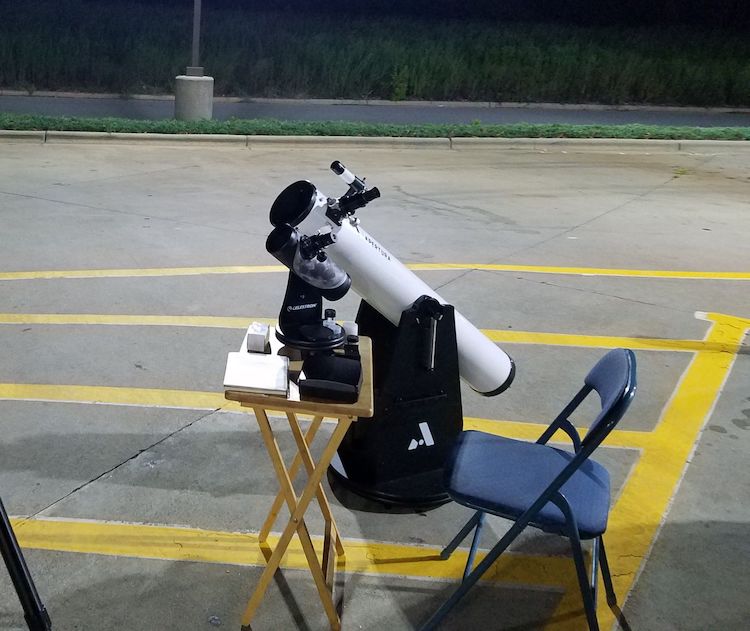

The Versatility of Dovetails
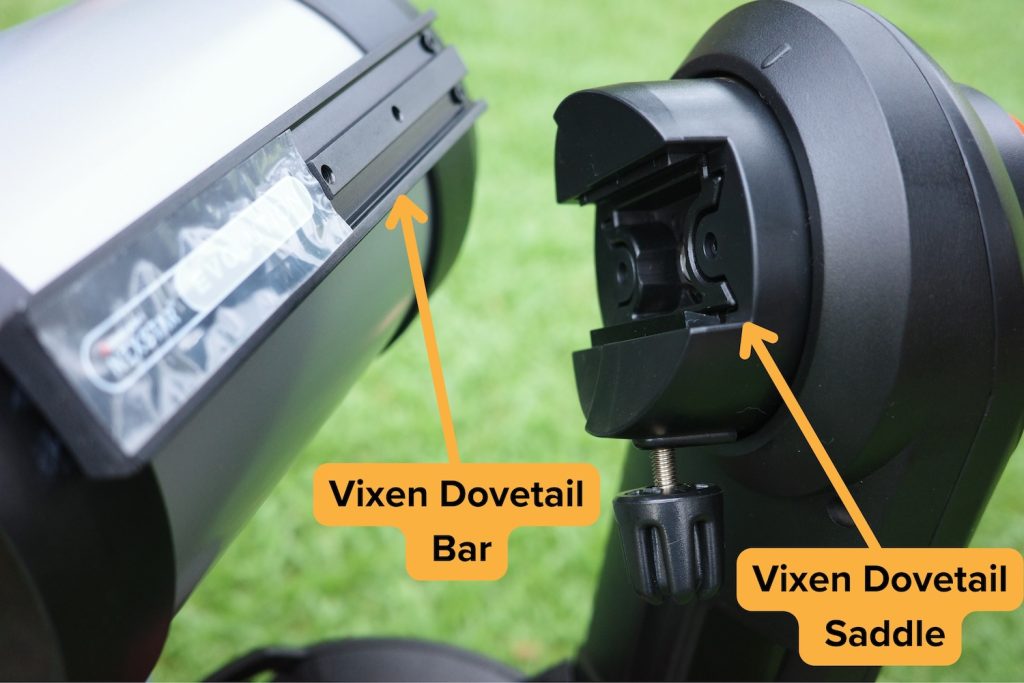
A very nice feature for a telescope to have is a Vixen Dovetail, which is a generic mounting standard that allows any telescope to be mounted on any compatible mount, regardless of manufacturer. Dovetails allow for your mount to accept a different telescope or for your telescope to be placed on a different mount, providing a potential upgrade path for your existing equipment.
It is not entirely necessary, though, and many beginner telescopes do not include this option or simply can’t due to the geometry of their mounts.
Unmounted or Handheld Telescopes
I would regret it if I didn’t at least mention handheld telescopes.
In addition to binoculars, some exceedingly cheap telescopes come with no mount at all. This is a huge red flag that what you’ve bought is simply a toy with poor optics.
There are exceptions:
- Handheld monoculars are essentially half of a pair of binoculars, and they can be found for very attractive prices (half that of an equivalent pair of binoculars, as you might imagine).
- And then there is the Galileoscope, a telescope kit originally sold at a loss for around 20 dollars (though it now goes for a much less attractive 80 dollars). To keep the costs very low, they do not provide a mount, only a ¼ 20 mounting washer for photo tripods.
A handheld telescope is severely limited in maximum magnification. Beyond about 15x, a handheld instrument becomes too shaky to use. I often find my lightweight 12×50 monocular difficult to use handheld when looking for sharp objects like Jupiter’s moons and craters on our moon, and using the Galileoscope handheld is nearly impossible.
